Abstract
Introduction: Indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas (iNHL), including follicular lymphoma (FL) and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), are slow-growing lymphoid malignancies with high response rates to first-line treatment, but most patients (pts) will eventually relapse after initial response to treatment. For those with refractory disease (relapse ≤ 6 months after ending treatment), outcomes are worse. A number of treatment options based on chemo- and/or immunotherapy exist for pts with relapsed/refractory (R/R) iNHL, but currently there is no single standard treatment approach. There is a need to better understand the reported efficacy of available systemic treatments for R/R FL and MZL to guide treatment of iNHL.
Methods: A SLR was carried out in accordance with PRISMA guidelines on September 1, 2017. Publications from MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and clinicaltrials.gov databases, as well as proceedings from the European Hematology Association and American Society of Clinical Oncology conferences held from 2015 to 2017, the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas from 2013, 2015, and 2017, and from the American Society of Hematology, and European Society for Medical Oncology conferences from 2014 to 2016, were included. Studies were limited to articles published in English, sample sizes ≥ 40, and studies evaluating systemic therapy for adults with any-stage R/R FL, MZL, or mixed histologies with ≥ 70% R/R FL/MZL pts. Controlled or uncontrolled clinical trials and observational studies were included. Studies varied with respect to prior treatment received and pt response to prior treatment at enrollment. Pts were classified as relapsed, refractory, refractory to rituximab (R-refractory including double-refractory pts), R/R but sensitive or naïve to rituximab, or as general R/R if the type of relapse and/or refractoriness was not specified. Efficacy measures included overall response rate, complete response rate, progression-free survival (PFS), and duration of response (DoR). Relevant interventions included bendamustine (B) (alone or with rituximab [BR] or obinutuzumab [O+B]), idelalisib (ID), ibrutinib (IB), copanlisib (C), lenalidomide (L) (alone or with rituximab [R2]), R + cyclophosphamide + doxorubicin + vincristine + prednisone (R-CHOP), R + cyclophosphamide + vincristine + prednisone (R-CVP), and R + chlorambucil (R-Chl).
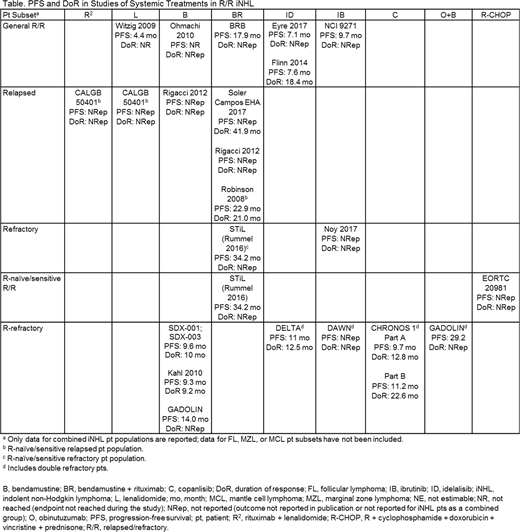
Results: Of 58 publications identified representing 36 studies involving 3,759 pts: 1 study reported on R2, 2 on L, 5 on B, 6 on BR, 3 on ID, 3 on IB, 2 on C, 1 on O+B, 1 on R-CHOP, and 12 on R alone. After excluding studies that did not meet criteria for similarity, 19 studies reporting outcomes in iNHL pts were included. Six studies each reported on general R/R pts or R-refractory pts, 4 studies reported on pts with relapsed disease, and 2 studies each reported on pts with refractory disease or R-naïve/sensitive refractory disease. PFS in the general R/R population (n = 1,668) ranged from 4.4 months (mo) in pts treated with L to 17.9 mo in pts treated with BR. Only 1 study reported DoR for pts in the general R/R population. In relapsed pts, PFS was only reported or reached in 1 study (22.9 mo) and DoR ranged from 21.0 to 41.9 mo for BR. In R-refractory pts, PFS ranged from 9.3 mo in B-treated pts to 29.2 mo in O+B-treated pts. DoR ranged from 9.2 to 22.6 mo. BR was investigated in the widest variety of disease subsets (4) with PFS ranging from 17.9 mo in the general R/R population to 34.2 mo in the R-naïve/sensitive R/R population (Table). Outcomes are likely to have been influenced by pt and disease characteristics (e.g., relapsed vs refractory, rituximab sensitive vs refractory, FL International Prognostic Index risk) and response criteria used (Cheson 1999, Cheson 2007, Laboratory of Experimental Oncology and Radiobiology [LEXOR], or unknown).
Conclusions: In pts with R/R iNHL (FL and MZL), there is significant variation in reported response and survival outcomes following systemic therapy. Currently, there is no clear standard of care for R/R iNHL, as demonstrated by the use of 9 different therapies across 19 studies identified in this SLR. Limited information is available on treatment outcomes for pts with different disease status and further studies are needed to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for specific subgroups of pts with R/R iNHL.
Bachy:Roche: Honoraria; Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Fox:Celgene: Consultancy, Other: travel support, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: travel support, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Sunesis: Consultancy. Howlett:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Snedecor:Celgene: Research Funding. Franek:Celgene Corp.: Consultancy. Zaidi:Celgene Corp.: Consultancy. Tabah:Celgene Corporation: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract